Multicriteria classification
In multiple criteria decision aiding (MCDA), multicriteria classification (or sorting) involves problems where a finite set of alternative actions should be assigned into a predefined set of preferentially ordered categories (classes).[1] For example, credit analysts classify loan applications into risk categories (e.g., acceptable/unacceptable applicants), customers rate products and classify them into attractiveness groups, candidates for a job position are evaluated and their applications are approved or rejected, technical systems are prioritized for inspection on the basis of their failure risk, etc.
Contents |
Problem statement
In a multicriteria classification problem (MCP) a set
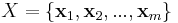
of m alternative actions is available. Each alternative is evaluated over a set of n criteria. The scope of the analysis is to assign each alternative into a given set of categories (classes) C={c1, c2, ..., ck}.
The categories are defined in an ordinal way. Assuming (without loss of generality) an ascending order, this means that category c1 consists of the best alternatives whereas c2 includes the worst (least preferred) ones. The alternatives in each category cannot be assumed be equivalent in terms of their overall evaluation (the categories are not equivalence classes).
Furthermore, the categories are defined independently of the set of alternatives under consideration. In that regard, MCPs are based on an absolute evaluation scheme. For instance, a predefined specific set of categories is often used to classify industrial accidents (e.g., major, minor, etc.). These categories are not related to a specific event under consideration. Of course, in many cases the definition of the categories is adjusted over time to take into consideration the changes in the decision environment.
Relationship to pattern recognition
In comparison to statistical classification and pattern recognition in a machine learning sense, two main distinguishing features of MCPs can be identified[2][3]:
- In MCPs the categories are defined in an ordinal way. This ordinal definition of the categories implicitly defines a preference structure. In contrast, machine learning is usually involved with nominal classification problems, where classes of observations are defined in a nominal way (i.e., collection of cases described by some common patterns), without any preferential implications.
- In MCPs, the alternatives are evaluated over a set of criteria. A criterion is an attribute that incorporates preferential information. Thus, the decision model should have some form of monotonic relationship with respect to the criteria. This kind of information is explicitly introduced (a priory) in multicriteria methods for MCPs.
Methods
The most popular modeling approach for MCPs are based on value function models, outranking relations, and decision rules:
- In a value function model, the classification rules can be expressed as follows: Alternative i is assigned to group cr if and only if
- where V is a value function (non-decreasing with respect to the criteria) and t1 > t2 > ... > tk-1 are thresholds defining the category limits.
- Examples of outranking techniques include the ELECTRE TRI method and its variants, models based on the PROMETHEE method, and the Proaftn method. Outranking models are expressed in a relational form. In a typical setting used in ELECTRE TRI, the assignment of the alternatives is based on pairwise comparisons of the alternatives to predefined category boundaries.
- Rule-based models are expressed in the form of "If ... then ... " decision rules. The conditions part involve a conjunction of elementary conditions on the set of criteria, whereas the conclusion of each rule provides a recommendation for the assignment of the alternatives that satisfy the conditions of the rule. The dominance-based rough set approach is an example of this type of models.
Model development
The development of MCP models can be made either through direct or indirect approaches. Direct techniques involve the specification of all parameters of the decision model (e.g., the weights of the criteria) through an interactive procedure, where the decision analyst elicits the required information from the decision-maker. This is can be a time-consuming process, but it is particularly useful in strategic decision making.
Indirect procedures are referred to as preference disaggregation analysis.[4] The preference disaggregation approach refers to the analysis of the decision–maker's global judgments in order to specify the parameters of the criteria aggregation model that best fit the decision-maker's evaluations. In the case of MCP, the decision–maker's global judgments are expressed by classifying a set of reference alternatives (training examples). The reference set may include: (a) some decision alternatives evaluated in similar problems in the past, (b) a subset of the alternatives under consideration, (c) some fictitious alternatives, consisting of performances on the criteria which can be easily judged by the decision-maker to express his/her global evaluation. Disaggregation techniques provide an estimate β* for the parameters of a decision model  based on the solution of an optimization problem of the following general form:
based on the solution of an optimization problem of the following general form:
where X is the set of reference alternatives, D(X) is the classification of the reference alternatives by the decision-maker, D'(X,fβ) are the recommendations of the model for the reference alternatives, L is a function that measures the differences between the decision-maker's evaluations and the model's outputs, and B is the set of feasible values for the model's parameters.
For example, the following linear program can be formulated in the context of a weighted average model V(xi)=w1xi1+...+wnxin with wj being the (non-negative) trade-off constant for criterion j (w1+...+wn=1) and xij being the data for alternative i on criterion j:
This linear programming formulation can be generalized in context of additive value functions.[5][6] Similar optimization problems (linear and nonlinear) can be formulated for outranking models,[7][8][9] whereas decision rule models are build through rule induction algorithms.
External links
References
- ^ Doumpos, M.; Zopounidis, C, (2002). Multicriteria Decision Aid Classification Methods. Heidelberg: Kluwer.
- ^ Doumpos, M.; Zopounidis, C. (2011). "Preference disaggregation and statistical learning for multicriteria decision support: A review". European Journal of Operational Research 209 (3): 203–214.
- ^ Waegeman, W.; De Baets, B.; Boullart, L. (2009). "Kernel-based learning methods for preference aggregation". 4OR 7 (2): 169–189.
- ^ Jacquet-Lagrèze, E.; Siskos, J. (2001). "Preference disaggregation: Twenty years of MCDA experience". European Journal of Operational Research 130 (2): 233–245.
- ^ Doumpos, M.; Zopounidis, C, (2002). Multicriteria Decision Aid Classification Methods. Heidelberg: Kluwer.
- ^ Köksalan, M.; Özpeynirci, B.S. (2009). "An interactive sorting method for additive utility functions". Computers and Operations Research 36: 2565–2572.
- ^ Doumpos, M.; Marinakis, Y.; Marinaki, M.; Zopounidis, C. (2009). "An evolutionary approach to construction of outranking models for multicriteria classification: The case of the ELECTRE TRI method". European Journal of Operational Research 199 (2): 496–505.
- ^ Mousseau, V.; Slowinski, R. (1998). "Inferring an ELECTRE-TRI model from assignment examples". Journal of Global Optimization 12 (2): 157–174.
- ^ Belacel, N.; Raval, H.; Punnen, A. (2007). "Learning multicriteria fuzzy classification method PROAFTN from data". Computers and Operations Research 34: 1885–1898.
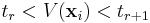
![\beta^*=\arg\min_{\beta\in B} L[D(X),D^'(X,f_{\beta})]](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/cc4a569a22279e1d261dcb2cb143d28f.png)
